Understanding Data Processing Systems
Data processing systems are fundamental to modern technology, forming the backbone of how information is collected, manipulated, and presented across various devices and applications. From everyday interactions with smartphones to complex scientific calculations, these systems are continually at work, transforming raw data into meaningful insights and actions. Grasping their core principles is key to understanding the digital world that surrounds us.
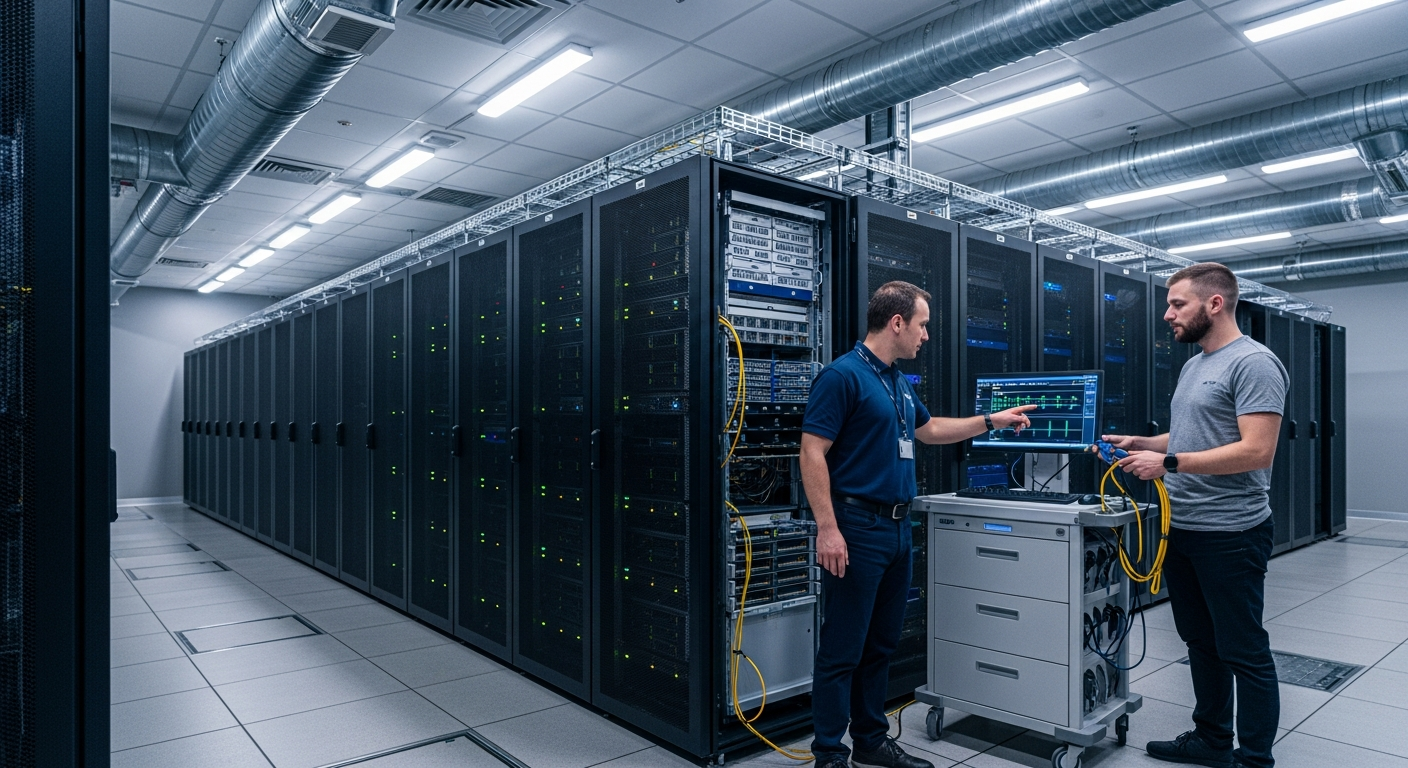

Data processing systems are integral to almost every aspect of contemporary life, orchestrating the conversion of raw data into valuable information. At its essence, data processing involves a series of operations performed on data to achieve a desired outcome. This systematic approach allows for the efficient management and utilization of vast amounts of information, driving decision-making and innovation across industries. The evolution of these systems has paralleled advancements in technology, making increasingly sophisticated tasks feasible.
The Role of Hardware in Processing
Hardware forms the physical foundation of any data processing system. This includes the central processing unit (CPU), memory (RAM), storage devices, and input/output devices. The CPU, often referred to as the brain of the computer, executes instructions and performs calculations, while RAM provides temporary storage for active data and programs, enabling quick access. Storage devices, such as hard drives and solid-state drives, are crucial for retaining data persistently. Various components and circuits work in concert to facilitate the rapid movement and manipulation of data, ensuring that processing operations are carried out swiftly and accurately. The design and architecture of these physical elements significantly impact a system’s overall performance and capabilities.
Software’s Contribution to Digital Operations
While hardware provides the physical infrastructure, software dictates how the hardware functions and how data is processed. Operating systems manage the computer’s resources and provide a platform for applications. Application software, ranging from word processors to complex analytical tools, performs specific tasks by instructing the hardware on what to do with the data. The interplay between hardware and software is critical; efficient software can optimize the use of hardware resources, leading to faster and more effective data processing. This symbiotic relationship is fundamental to all digital operations, from simple data entry to advanced machine learning algorithms.
Data Storage and Retrieval Methods
Effective storage and retrieval mechanisms are paramount for any data processing system. Data can be stored in various formats and locations, including local drives, network-attached storage, and cloud-based solutions. The choice of storage method often depends on factors such as data volume, access speed requirements, security needs, and cost. Efficient retrieval methods, facilitated by databases and file systems, ensure that processed information can be accessed quickly and reliably when needed. Modern systems often employ sophisticated indexing and caching techniques to optimize data access times, which is vital for applications requiring real-time data analysis or rapid information display.
Connectivity and Display Technologies
Connectivity is another essential aspect, enabling data to be shared and accessed across different devices and networks. Wired and wireless technologies, such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and cellular networks, provide the pathways for data transmission. This interconnectedness allows for distributed processing, where tasks are spread across multiple machines, and facilitates collaboration and remote access to information. Displays serve as the primary output interface, presenting processed data to users in a visually comprehensible format. The quality and type of display technology can significantly impact user experience, particularly in applications that rely heavily on visual data, such as graphic design, scientific visualization, or gaming. Continuous innovation in display and connectivity technologies further enhances the capabilities and reach of data processing systems.
Types of Processing Systems and Their Applications
Data processing systems come in many forms, each suited for different applications. Transaction processing systems (TPS) handle routine business transactions, such as order entry or payroll. Batch processing systems collect data over a period and process it together, often used for tasks like billing. Real-time processing systems handle data as it arrives, critical for applications like air traffic control or online banking. Distributed processing systems utilize multiple interconnected computers to process data, improving efficiency and reliability. The choice of system depends on the specific requirements of the task, including data volume, processing speed, and desired output. Understanding these distinctions helps in designing and implementing effective computing solutions for diverse needs.
Data processing systems are the unseen engines driving the digital world. Their continuous evolution, propelled by advancements in hardware and software, along with sophisticated storage and connectivity solutions, underpins nearly every technological interaction. From the individual use of gadgets to large-scale industrial operations, these systems are constantly refining how data is managed, transformed, and ultimately utilized to create value and foster innovation globally.