The Role of Fiber Optics in Global Data Transport
Fiber optic technology has fundamentally reshaped how information travels across the globe, serving as the indispensable backbone of modern digital communication. Its unique properties allow for the transmission of vast amounts of data at unprecedented speeds, enabling everything from real-time international video calls to complex cloud computing services. Understanding the critical function of fiber optics illuminates its profound impact on our interconnected world, facilitating global connectivity and driving technological progress across various sectors, from telecommunications to scientific research and everyday internet usage.
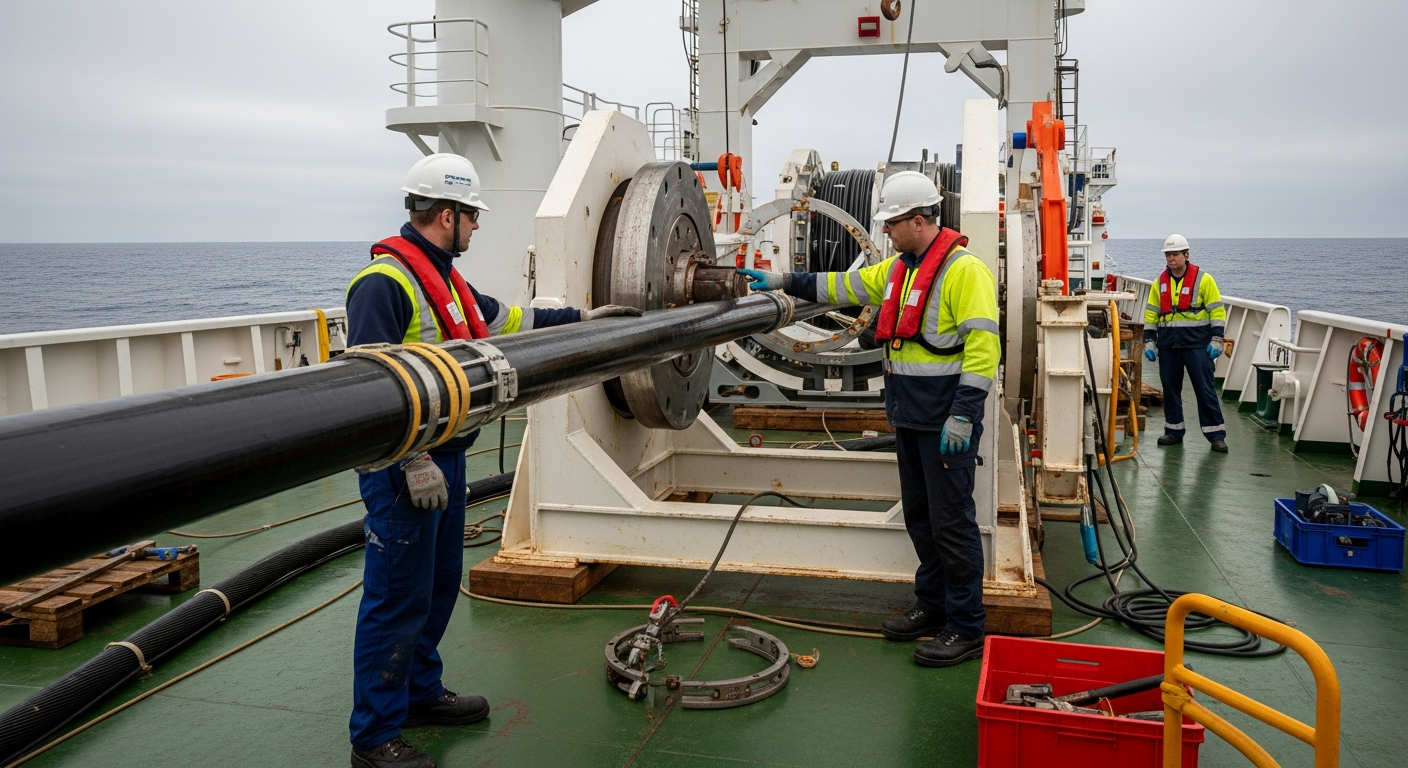

How Fiber Optics Revolutionized Global Connectivity and Communication?
The advent of fiber optic technology marked a pivotal shift in global connectivity and communication. Before fiber, copper cables were the primary medium for transmitting data, but they suffered from significant limitations in terms of speed, bandwidth, and signal degradation over distance. Fiber optics, utilizing thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit light signals, overcame these challenges. This innovation enabled the creation of high-capacity data highways, forming the bedrock of the internet and facilitating seamless international data exchange. The ability to send information across continents with minimal loss has transformed how businesses operate, how individuals communicate, and how societies access information, truly digitalizing global interactions.
What are the Core Advantages of Fiber Optic Technology for Data Transport?
Fiber optic technology offers several distinct advantages that make it superior for modern data transport. Firstly, its capacity for high speed is unparalleled, allowing data to travel at nearly the speed of light. Secondly, fiber cables provide immense bandwidth, meaning they can carry a significantly larger volume of data simultaneously compared to traditional copper wires. This is crucial for supporting bandwidth-intensive applications like streaming high-definition video and cloud services. Furthermore, fiber optics exhibit very low signal attenuation and are immune to electromagnetic interference, which ensures greater reliability and signal integrity over long distances. These characteristics contribute to a more stable and efficient network, essential for the demanding needs of current digital systems.
How Does Fiber Optic Infrastructure Support Modern Digital Networks?
The infrastructure built upon fiber optics is the unseen foundation of modern digital networks worldwide. Submarine fiber optic cables crisscross ocean floors, connecting continents and enabling global communication on an unprecedented scale. Terrestrial fiber networks extend these connections inland, linking cities, data centers, and critical infrastructure. This extensive network forms a resilient and high-capacity system that supports everything from financial transactions and scientific collaborations to online gaming and social media. Without this robust fiber infrastructure, the digital economy and the interconnectedness we experience daily would be impossible, highlighting its role in supporting diverse digital systems.
What is the Impact of Fiber Optics on Broadband Access and Wireless Systems?
Fiber optics plays a crucial role in delivering high-speed broadband access to homes and businesses, transforming local services and user experiences. Fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployments provide direct, ultra-fast internet connections, enabling advanced applications and services. Beyond wired connections, fiber also serves as the critical backhaul for wireless systems. Modern cellular networks, including 5G and future generations, rely heavily on fiber optic cables to connect cell towers to the core network. This ensures that the vast amounts of data generated by wireless devices can be transmitted quickly and efficiently, providing the necessary bandwidth and speed for mobile communication and other wireless technologies.
Ensuring Security and Fostering Innovation in Fiber Optic Networks
Security is a paramount concern in data transport, and fiber optic networks offer inherent advantages in this area. Unlike copper cables, which can be more easily tapped to intercept electrical signals, fiber optic cables are significantly harder to compromise without detection. Any attempt to physically tap into a fiber cable typically causes a noticeable disruption in the light signal, making unauthorized access more challenging to conceal. Furthermore, the field of fiber optics continues to be a hotbed for innovation. Researchers and engineers are constantly developing new technologies, such as wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) and spatial division multiplexing, to further increase bandwidth and speed, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in global data transport and helping to further digitalize societies.
Fiber optic technology has undeniably become the backbone of global data transport, enabling the high-speed, high-bandwidth connectivity that underpins our modern digital world. From facilitating international communication to driving the capabilities of broadband and wireless systems, its advantages in speed, reliability, and security are unmatched. As the demand for data continues to grow exponentially, the ongoing innovation in fiber optics ensures its continued relevance and indispensable role in shaping the future of global connectivity and digital transformation.