Space Exploration: The Next Frontier of Human Travel
Humanity's innate curiosity has always driven us to explore beyond our immediate surroundings, from ancient voyages across oceans to the pioneering flights that conquered the skies. Today, this spirit of adventure is increasingly focused on the vast expanse of space. What was once the exclusive domain of national space agencies and science fiction is rapidly evolving into a realm of potential for broader human engagement. This expansion promises not only scientific discovery but also a profound reshaping of our understanding of travel, mobility, and our place in the cosmos. As technologies advance and commercial ventures gain traction, the concept of space travel is transitioning from an abstract dream to a tangible, albeit challenging, frontier.
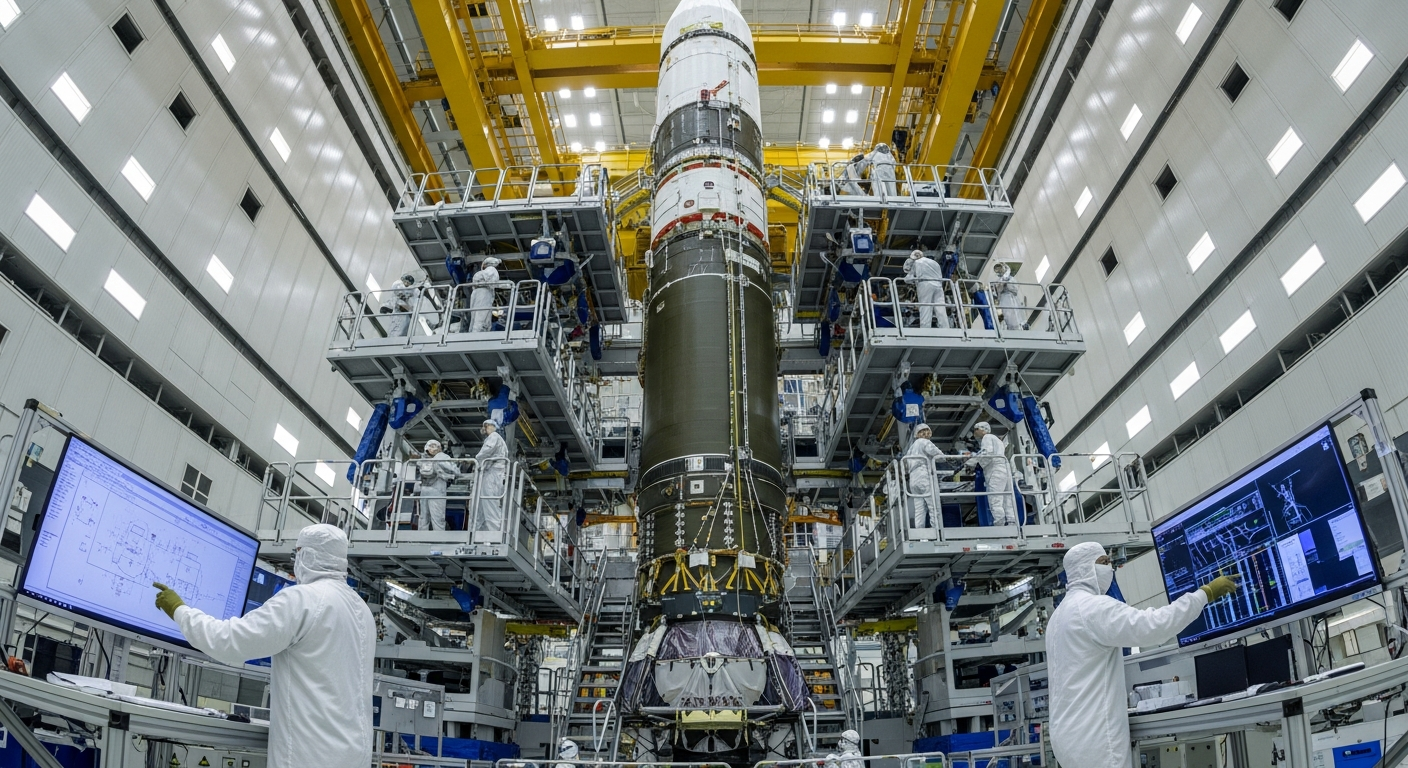

The Evolution of Space Mobility
Space mobility encompasses a wide range of activities, from orbital tourism to long-duration missions to other celestial bodies. Initially, space travel was characterized by government-funded programs focused on scientific research and national prestige. Projects like Apollo and the International Space Station (ISS) demonstrated the incredible feats human ingenuity could achieve. However, recent decades have witnessed a significant shift with the emergence of private companies. These entities are developing reusable rockets and innovative spacecraft, aiming to reduce the cost and increase the frequency of launches, thereby opening up space to a wider array of participants and purposes. This commercialization is a critical factor in the ongoing evolution of how we move beyond Earth.
Human Journeys and Space Exploration
Space exploration represents the ultimate journey, pushing the boundaries of human endurance and technological capability. Future human journeys into space are envisioned to extend far beyond low Earth orbit. Plans include establishing permanent bases on the Moon, facilitating exploration of Mars, and potentially even ventures to asteroids. These ambitious projects require not only advanced propulsion systems but also sophisticated life support, radiation shielding, and psychological support for crews on extended missions. The data gathered from these journeys will provide invaluable insights into the origins of our solar system, the potential for extraterrestrial life, and the resources available beyond Earth.
Logistics and Routes in Space Travel
Effective logistics are paramount for any form of travel, and space travel presents unique challenges. Planning routes in space involves complex orbital mechanics, considering factors such as gravitational pulls, planetary alignments, and fuel efficiency. Supplying spacecraft and future off-world habitats requires intricate supply chains, transporting everything from food and water to spare parts and scientific equipment. Developing autonomous systems for resupply and maintenance, as well as in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) – using local materials on the Moon or Mars – are key areas of focus to make long-term space presence viable and sustainable.
The Future of Sustainable Space Travel
Sustainability is a growing concern for all forms of travel, and space is no exception. As space activity increases, so does the amount of orbital debris, posing a risk to operational satellites and spacecraft. Efforts are underway to develop technologies for debris removal and to implement regulations for responsible space operations. Furthermore, the concept of sustainable space travel extends to minimizing the environmental impact of rocket launches on Earth and exploring cleaner propulsion methods. Developing closed-loop life support systems for habitats and utilizing renewable energy sources in space are crucial steps toward ensuring a long-term, responsible human presence beyond our home planet.
Space Vehicles and Advanced Propulsion
The development of advanced space vehicles and propulsion systems is central to expanding human reach into space. Current rockets primarily rely on chemical propulsion, which is effective but limits the speed and payload capacity for deep-space missions. Research into innovative propulsion technologies, such as electric propulsion (ion thrusters), nuclear thermal propulsion, and even theoretical concepts like warp drives, aims to drastically reduce travel times and increase efficiency. Alongside propulsion, the design of spacecraft is evolving to include more comfortable and adaptable habitats for crew, capable of withstanding the harsh conditions of space while supporting human well-being during extended voyages. Advances in materials science are also contributing to lighter, stronger, and more protective vehicle structures.
New Destinations and Space Adventure
The allure of new destinations drives the spirit of adventure in space exploration. Beyond the Moon and Mars, scientists and enthusiasts look towards asteroids as potential sources of resources and unique scientific study. The moons of Jupiter and Saturn, with their subsurface oceans, offer tantalizing possibilities for discovering life. For individuals, the initial phase of space adventure is likely to be suborbital or orbital tourism, offering unparalleled views of Earth. As technology matures, more extensive journeys, perhaps to lunar resorts or Martian outposts, could become accessible, transforming the definition of a global movement and offering experiences previously confined to imagination.
Space exploration is a testament to human ambition and our continuous drive to understand the universe. It represents a complex interplay of science, engineering, and human spirit, promising not only to expand our knowledge but also to redefine the very nature of human travel and our connection to the cosmos.