Intercontinental Movement: Systems and Impact
Intercontinental movement represents the intricate web of systems that enable people and goods to traverse vast distances across the globe. From ancient trade routes to modern air travel, the ability to connect continents has profoundly shaped human civilization, economies, and cultures. Understanding the underlying infrastructure, diverse modes of transport, and the complex logistics involved is essential to appreciating the scale and significance of global connectivity in today's interconnected world. This extensive network facilitates everything from personal journeys and business mobility to global trade and cultural exchange, continually evolving with technological advancements and shifting demands.

Intercontinental Journeys and Global Mobility
Intercontinental journeys form the backbone of global connectivity, allowing individuals and groups to experience diverse cultures, engage in international commerce, and pursue new opportunities. The concept of global mobility extends beyond mere physical movement; it encompasses the societal, economic, and cultural shifts enabled by the seamless passage of people across continents. Historically, such voyages were arduous feats of exploration, driven by curiosity, trade, or conquest. Today, modern systems have transformed these journeys into routine occurrences for millions, fostering a deeper understanding of our interconnected world and supporting a globalized economy. The motivations for these movements are varied, ranging from leisure travel and family visits to professional assignments and educational pursuits, all contributing to a dynamic global landscape.
Core Transit Systems and Infrastructure
The infrastructure supporting intercontinental movement is vast and complex, comprising a network of transit systems designed to facilitate efficient passage. Key components include international airports, major seaports, and, in some cases, extensive rail networks connecting large landmasses. These hubs serve as critical nodes where passengers and cargo transfer between different modes of transport. The development of robust infrastructure, including advanced navigation systems, communication technologies, and logistical frameworks, is paramount to ensuring the smooth flow of global traffic. Various vehicles, from wide-body aircraft to large container ships, are specifically engineered for long-haul travel, forming the operational core of these intricate transit operations. Effective planning and coordination are essential to manage the immense volume of movement.
Aviation’s Role in Passenger Movement
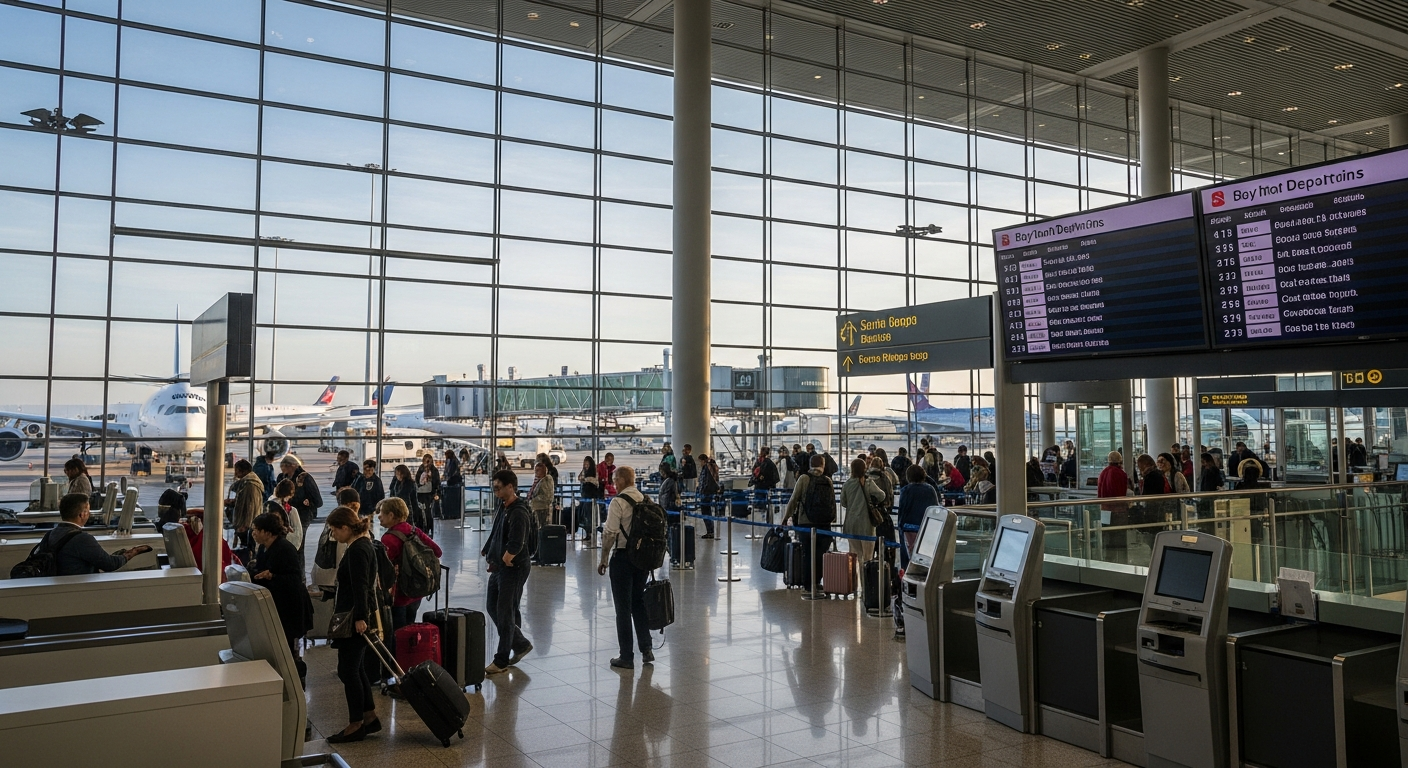
Aviation stands as a cornerstone of modern intercontinental passenger travel, offering unparalleled speed and direct access to distant destinations. The global network of air routes connects virtually every major city, enabling rapid transit across oceans and continents. This mode of transport has significantly reduced travel times, making a global voyage more accessible for business professionals, tourists, and individuals maintaining international connections. The management of aviation involves sophisticated air traffic control systems, international agreements, and a vast array of support services to ensure safety and efficiency. Airlines operate complex schedules, managing passenger flows and baggage logistics, making air travel a highly coordinated and technologically advanced form of global movement.
Logistics, Trade, and Exploration
Beyond passenger transport, intercontinental logistics play a critical role in global trade, enabling the movement of goods and resources across vast distances. Supply chains that span continents rely heavily on efficient freight forwarding, multimodal transport, and sophisticated tracking systems. This aspect of global movement facilitates the distribution of products from manufacturers to markets worldwide, underpinning international commerce. Historically, such logistical capabilities were integral to exploration, allowing empires and merchants to extend their reach. Today, advanced logistics continue to drive economic growth and foster innovation by connecting producers and consumers globally, making diverse goods accessible in various markets and supporting complex industrial processes.
Planning Intercontinental Routes
Effective planning is crucial for any intercontinental route, whether it’s a personal voyage or a recurring professional commute. Considerations include the choice of vehicle (e.g., aircraft, cruise ship), the most efficient or convenient route, necessary travel documents, and logistical arrangements at the destination. Travelers often evaluate factors such as travel time, cost, comfort, and directness of the route. For frequent international commuters, optimizing travel schedules and understanding global transit regulations are key. Technology, through online booking platforms and travel management tools, has simplified the process of identifying optimal routes and managing the complexities associated with crossing multiple time zones and international borders, making global movement more streamlined than ever before.
General Cost Considerations for Global Travel
The cost of intercontinental travel varies significantly based on numerous factors, including the mode of transport, the class of service, the distance covered, and the time of year. Air travel, for instance, can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars depending on whether one opts for economy, business, or first class, and whether booking occurs well in advance or last-minute. Similarly, sea travel, such as cruises or cargo ship passages, also presents a wide spectrum of pricing. Other influencing factors include the popularity of the destination, the duration of the trip, and any additional services like premium seating, extra baggage, or travel insurance. It is advisable to research thoroughly and compare options across different providers and booking periods to find suitable arrangements within a budget.
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Impact of Intercontinental Movement
Intercontinental movement exerts a profound impact on various facets of global society, ranging from economic development to environmental considerations. Economically, it drives tourism, facilitates trade, and supports global supply chains, creating jobs and fostering international investment. Culturally, it promotes exchange and understanding between diverse populations, enriching societies through shared experiences and ideas. However, this extensive movement also presents challenges, including environmental concerns related to carbon emissions from aviation and shipping, and the potential for the rapid spread of diseases. Addressing these impacts requires ongoing innovation in sustainable transport technologies and international cooperation to manage the complexities of a highly interconnected world while striving for a balanced approach to global mobility.