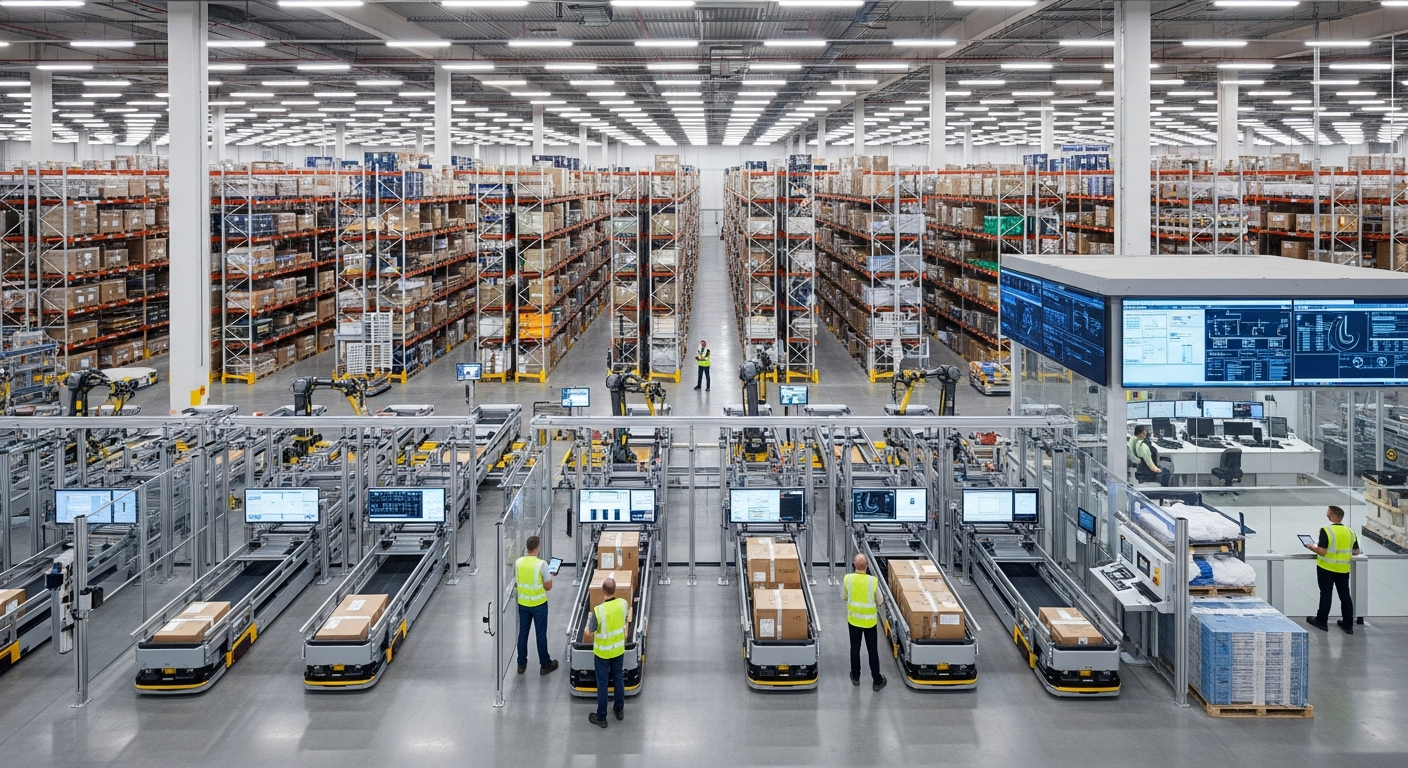
Innovation in Material Science for Production
Material science plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of industrial production by introducing novel properties and functionalities. Advances in this field are not merely incremental; they represent fundamental shifts in how products are designed, manufactured, and ultimately perform. From lightweight composites to smart materials, these innovations are driving significant transformations across various sectors, influencing everything from product longevity to environmental impact and operational efficiency in manufacturing processes globally.
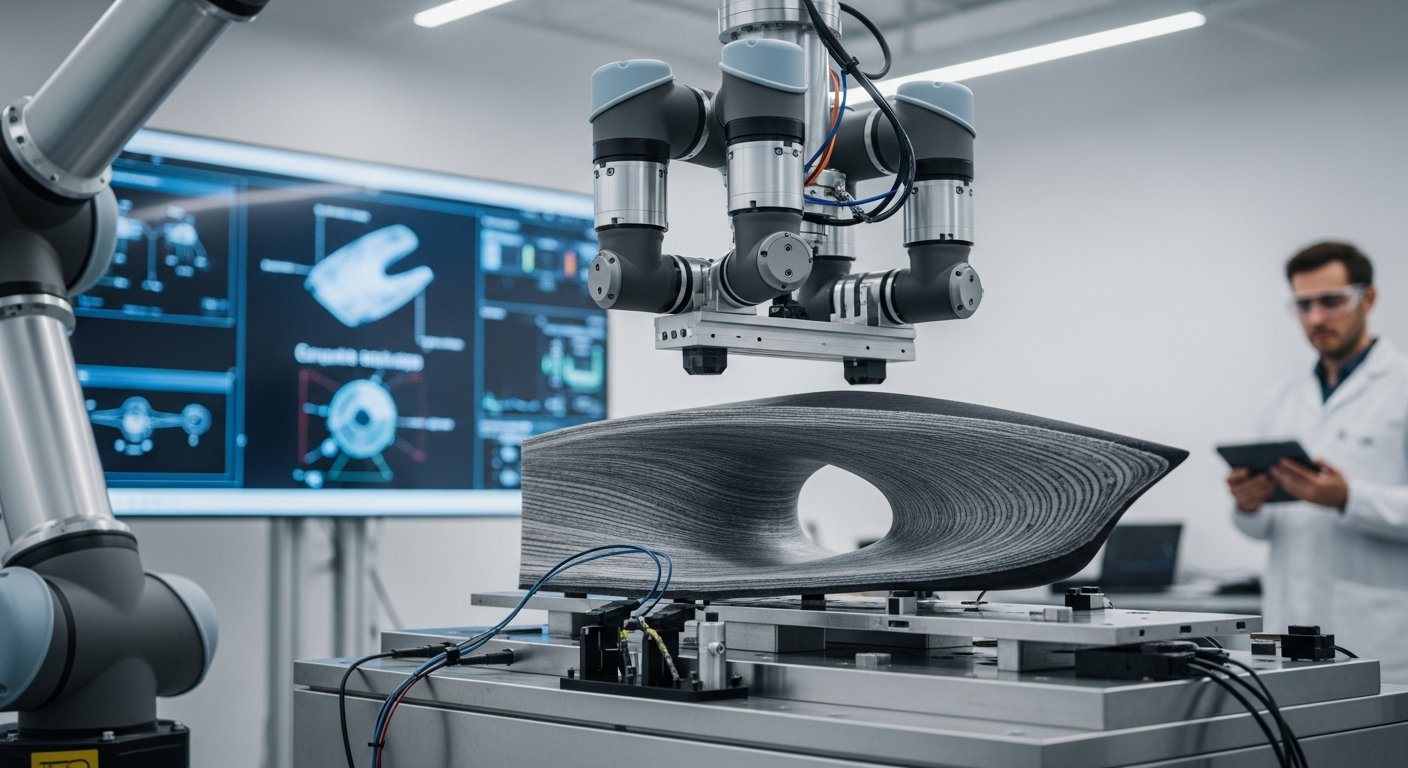

How do Advanced Materials Drive Manufacturing Evolution?
Advanced materials are at the forefront of the ongoing evolution in manufacturing. These materials, encompassing everything from high-performance alloys and ceramics to polymers and composites, offer properties that traditional materials cannot match. Their development is driven by the need for products that are lighter, stronger, more durable, and often more specialized. This directly impacts production methodologies, requiring new processes and technologies to handle and integrate these materials effectively. The continuous pursuit of superior material performance directly influences the design and engineering phases, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in various industries.
Enhancing Efficiency and Sustainability Through Material Innovation
Material innovation significantly contributes to enhancing both operational efficiency and sustainability in production. For instance, the development of materials with improved strength-to-weight ratios can lead to lighter components, which in turn reduces energy consumption during transportation and operation. Similarly, new materials designed for greater durability can extend product lifespans, reducing waste and the need for frequent replacements. Innovations in sustainable materials, such as bio-based plastics or recycled composites, also play a crucial role in minimizing environmental footprints, aligning production processes with global sustainability goals. This focus on material properties directly supports more efficient resource utilization and reduced environmental impact throughout the entire product lifecycle.
The Role of Digitalization and Automation in Material Processes
Digitalization and automation are integral to harnessing the full potential of advanced materials in production. Digital tools, including advanced simulation software and data analytics platforms, enable engineers to predict material behavior more accurately, optimize designs, and streamline prototyping. Automation, through robotics and advanced manufacturing systems, facilitates the precise handling, processing, and assembly of complex materials, often in environments unsuitable for human workers. This integration of technology ensures consistency, reduces errors, and accelerates the pace of innovation from the laboratory to the production floor. The synergy between new materials and digital technologies is crucial for modern enterprise systems, enabling sophisticated control over manufacturing operations and processes.
Impact on Global Supply Chains and Workforce Development
Innovations in material science have profound implications for global supply chains and workforce development. The introduction of specialized materials can necessitate new sourcing strategies, potentially shifting reliance on certain regions or requiring the development of new extraction or synthesis methods. This also impacts logistics, as some advanced materials may require specific handling or transportation conditions. Concurrently, the evolving landscape of material science demands a skilled workforce capable of working with these new materials and the advanced technologies used to process them. This drives the need for continuous training and development programs to equip the workforce with the necessary expertise in areas like advanced manufacturing, data analytics, and robotics, ensuring that human capital can keep pace with technological advancements.
Future Outlook: Robotics, Analytics, and Enterprise Systems
Looking ahead, the intersection of material science with robotics, analytics, and sophisticated enterprise systems will continue to drive significant advancements in production. Robotics will become even more adept at manipulating and processing delicate or complex materials, while advanced analytics and data will provide deeper insights into material performance and process optimization. Integrated enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES) will leverage this data to create more agile and responsive production environments. This holistic approach, combining material innovation with smart systems, will enable manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, quality, and adaptability, further solidifying the role of technology and innovation in global production operations.
Advancements in Material Development Technologies
Various entities contribute to the advancement of material science for production, ranging from research institutions to specialized industrial manufacturers. These organizations focus on different aspects of material development, including synthesis, characterization, and application engineering. Their collaborative efforts often involve extensive research and development, aiming to create materials that address specific industrial challenges, such as enhancing component longevity or reducing environmental impact. The continuous investment in research and development by these providers is crucial for introducing new materials into the global production landscape and fostering ongoing innovation in the field.
Material science innovation is a dynamic field that continually reshapes industrial production. By introducing novel materials and leveraging advanced technologies like digitalization, automation, and robotics, industries can achieve greater efficiency, sustainability, and adaptability. The ongoing development in this area promises further advancements that will continue to redefine manufacturing capabilities and global operational strategies for years to come.