Enhancing Data Security Through Hardware Innovations
In an increasingly interconnected world, the integrity and confidentiality of data are paramount. While software solutions often receive significant attention in the realm of cybersecurity, the foundational role of hardware in establishing robust security measures is becoming ever more critical. Hardware innovations are continuously evolving to create more secure computing environments, offering protection at the very core of digital systems and complementing software-based defenses.
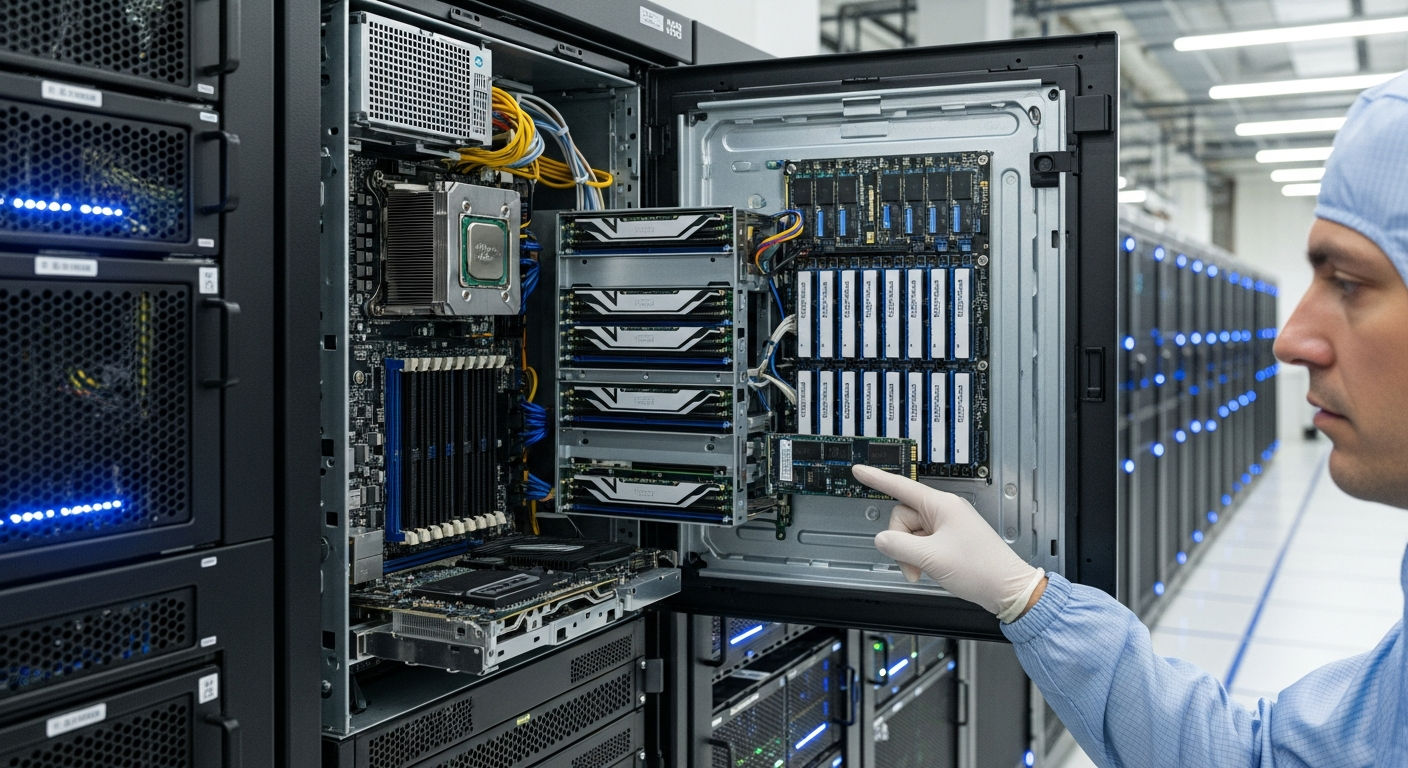

Foundational Hardware for Digital Security
The bedrock of any secure digital system lies within its fundamental hardware components. The processor, often considered the brain of a computing device, plays a crucial role in data security. Modern processors incorporate features like secure boot mechanisms, which verify the integrity of the operating system before it loads, preventing malicious software from hijacking the boot process. Embedded cryptographic engines within the semiconductor architecture accelerate encryption and decryption operations, making it feasible to secure data without significant performance overhead. These components are designed to create a trusted execution environment, isolating sensitive operations from the rest of the system and protecting critical data and code from unauthorized access or tampering.
Memory and Storage Protections
Data security extends beyond processing to how information is stored and accessed. Innovations in memory and storage hardware are vital for safeguarding sensitive data. Secure memory architectures, for instance, employ techniques like memory encryption and access control to prevent unauthorized reading or modification of data residing in RAM. For persistent data, secure storage devices utilize self-encrypting drives (SEDs) that automatically encrypt all data written to them. This hardware-level encryption ensures that even if a storage device is physically removed from a system, its contents remain unreadable without the correct authentication keys. These device-level security features are essential for protecting information throughout its lifecycle, from active use in memory to long-term storage.
Advanced Hardware Security Innovations
The landscape of hardware security is continually advancing, driven by ongoing innovation and emerging threats. Technologies like Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs) are specialized semiconductor components that provide hardware-based security functions, including secure key generation, storage, and authentication. These modules enhance device integrity by verifying system configurations and protecting sensitive cryptographic material. Furthermore, the burgeoning field of quantum computing, while still in its early stages, also presents future security considerations and opportunities. Research into quantum-resistant cryptography involves developing algorithms that can withstand attacks from future quantum computers, with hardware implementations being a key area of focus. These advanced hardware-based approaches offer a strong defense against sophisticated digital threats.
The Role of Secure Interfaces and Networks
Security also encompasses how hardware interacts with its environment and other systems. Secure interfaces are crucial for preventing data interception or manipulation as it travels between components or external devices. This includes secure communication protocols implemented at the hardware level, protecting data as it moves across a network. Sensor technology, while often associated with data collection, also plays a role in physical security, detecting unauthorized access or tampering with hardware. Furthermore, the integration of security features into network hardware, such as routers and switches, helps establish secure communication channels and protect data in transit. The continuous evolution of hardware in these areas is critical for maintaining robust security across complex computing environments.
Sustainable Security Through Hardware Design
Beyond direct security functions, considerations for sustainable hardware design can indirectly contribute to long-term security. Developing hardware components that are durable, energy-efficient, and designed for longevity reduces the frequency of hardware replacements, which can introduce new vulnerabilities during transitions. A focus on robust component manufacturing and supply chain transparency, often linked with sustainable practices, helps mitigate the risk of counterfeit or compromised hardware entering the digital ecosystem. This holistic approach to hardware development supports not only environmental goals but also strengthens the overall security posture of computing infrastructure over time.
In summary, the ongoing evolution of hardware innovations is fundamental to enhancing data security in the digital age. From secure processors and memory to advanced cryptographic modules and protected network interfaces, hardware provides a critical layer of defense against an array of cyber threats. By embedding security features directly into the physical components of computing systems, these innovations create a more resilient and trustworthy environment for data, forming an essential counterpart to software-based security measures.