Cryotherapy: The Cold Truth About Beauty's Coolest Trend
In the ever-evolving world of beauty and wellness, a frosty newcomer has been sending shivers down the spines of enthusiasts and skeptics alike. Cryotherapy, once reserved for elite athletes and medical treatments, has burst onto the mainstream scene with promises of rejuvenation, pain relief, and even weight loss. This icy intervention involves exposing the body to extremely low temperatures for short periods, typically in a specially designed chamber or through localized applications. As more spas and wellness centers add cryotherapy to their menus, it's time to dive deep into the cold, hard facts about this chilling trend that's heating up the beauty industry.
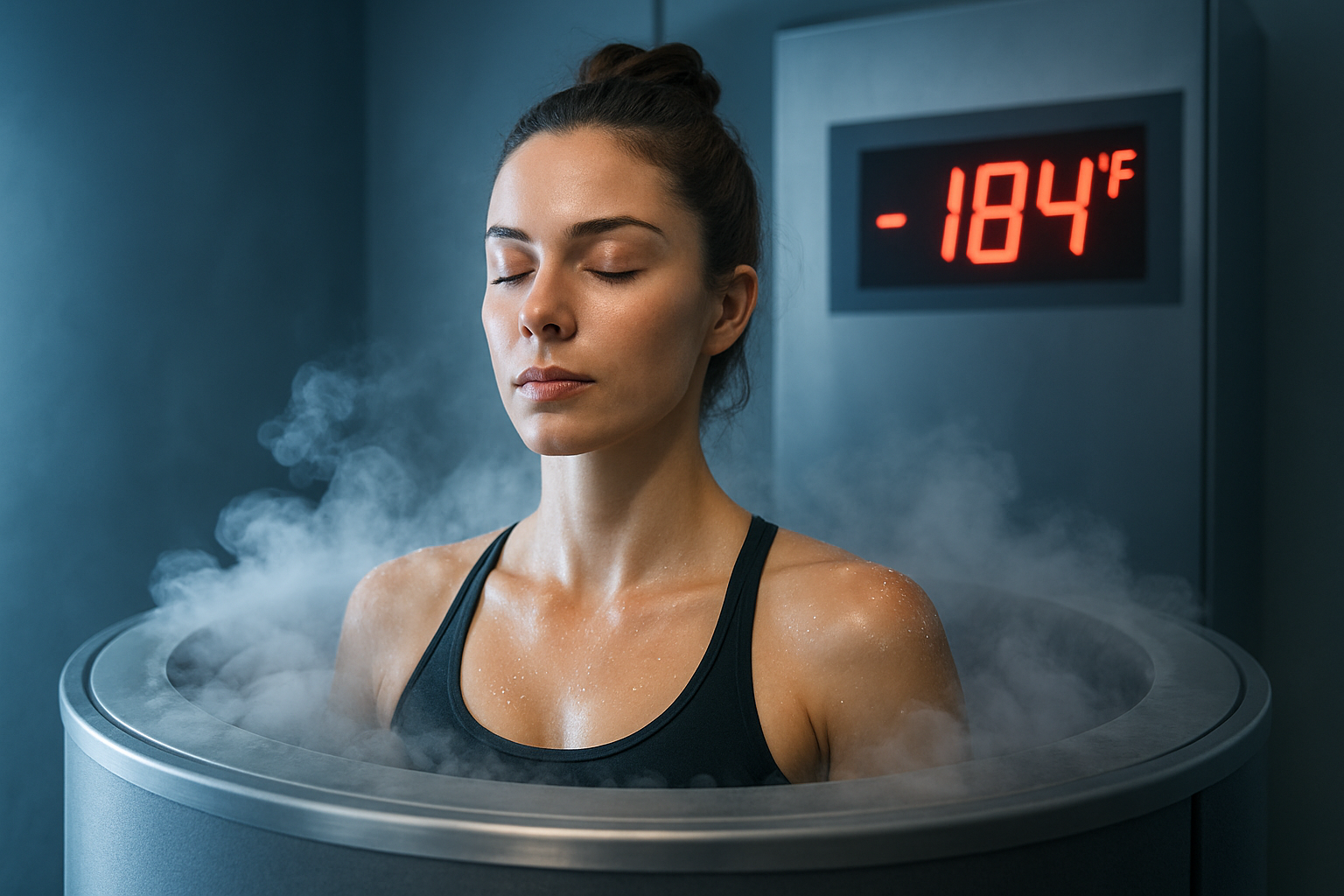

The process involves standing in a cryochamber for two to four minutes while liquid nitrogen-cooled air circulates at temperatures between -200°F and -300°F (-129°C to -184°C). Localized cryotherapy can also be applied to specific areas using wands or other devices. The theory behind the treatment is that extreme cold triggers the body’s natural healing mechanisms, leading to a range of potential benefits.
The Science of the Shiver: How Cryotherapy Works
When exposed to extreme cold, the body’s blood vessels constrict, redirecting blood flow to vital organs. This process, known as vasoconstriction, is believed to reduce inflammation and flush out toxins. As the body warms up post-treatment, blood rushes back to the extremities, potentially delivering oxygen and nutrients more efficiently.
Proponents of cryotherapy claim that this process can boost metabolism, improve skin tone, reduce muscle soreness, and even enhance mood. The release of endorphins and the stimulation of the nervous system during cryotherapy are thought to contribute to these effects. However, it’s important to note that while some studies support these claims, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects and efficacy of cryotherapy.
Beauty on Ice: Cryotherapy’s Cosmetic Applications
In the beauty world, cryotherapy has found its niche in both professional treatments and at-home devices. Cryofacials, which involve applying cold temperatures to the face, are touted as a non-invasive alternative to more aggressive skin treatments. The cold is said to tighten pores, increase collagen production, and reduce puffiness.
Cryolipolysis, a fat-reduction technique that uses controlled cooling to eliminate fat cells, has also gained popularity. This procedure, often known by the brand name CoolSculpting, targets specific areas of the body and is marketed as a non-surgical alternative to liposuction.
At-home cryotherapy tools, such as ice rollers and cold therapy masks, have flooded the market, promising to bring the benefits of professional treatments to the comfort of one’s home. These devices claim to reduce under-eye bags, soothe irritated skin, and even help with product absorption.
The Cold Hard Truth: Risks and Controversies
Despite its growing popularity, cryotherapy is not without its critics and concerns. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved whole-body cryotherapy for any medical use, citing a lack of evidence for its purported health benefits. There are also potential risks associated with the treatment, including frostbite, burns, and oxygen deficiency if not properly administered.
Some experts argue that the effects of cryotherapy are largely placebo-driven and that similar benefits can be achieved through less extreme methods, such as ice baths or cold showers. Critics also point out that many of the studies supporting cryotherapy have been small-scale or funded by companies with a vested interest in the technology.
Moreover, the accessibility and regulation of cryotherapy services vary widely. With the treatment becoming more mainstream, there are concerns about untrained personnel operating cryotherapy equipment and the potential for misuse or accidents.
Chilling Predictions: The Future of Cryotherapy in Beauty
As the beauty industry continues to embrace technology and innovation, cryotherapy is likely to evolve and expand its applications. Research into the long-term effects of regular cryotherapy use may provide more concrete evidence for or against its purported benefits. This could lead to more targeted treatments and potentially FDA approval for specific uses.
The development of more sophisticated at-home cryotherapy devices could democratize access to the treatment, allowing users to incorporate cold therapy into their daily routines. However, this also raises questions about safety and efficacy outside of controlled environments.
As consumers become more educated about wellness treatments, there may be a push for greater regulation and standardization in the cryotherapy industry. This could lead to more rigorous training requirements for operators and clearer guidelines for treatment protocols.
In conclusion, cryotherapy represents a fascinating intersection of ancient healing practices and modern technology in the beauty and wellness space. While its icy allure continues to captivate those seeking the fountain of youth and peak physical performance, it’s clear that more research and regulation are needed to separate the cold, hard facts from the frosty fiction. As the industry evolves, consumers would do well to approach cryotherapy with a cool head, weighing the potential benefits against the risks and consulting with healthcare professionals before taking the plunge into sub-zero beauty treatments.