Circadian Fasting: Aligning Nutrition with Your Body Clock
Imagine a world where your meal times are as crucial as what you eat. A realm where the simple act of timing your meals could revolutionize your health, energy levels, and overall well-being. Welcome to the fascinating world of circadian fasting, a cutting-edge approach that marries nutritional science with our body's natural rhythms.
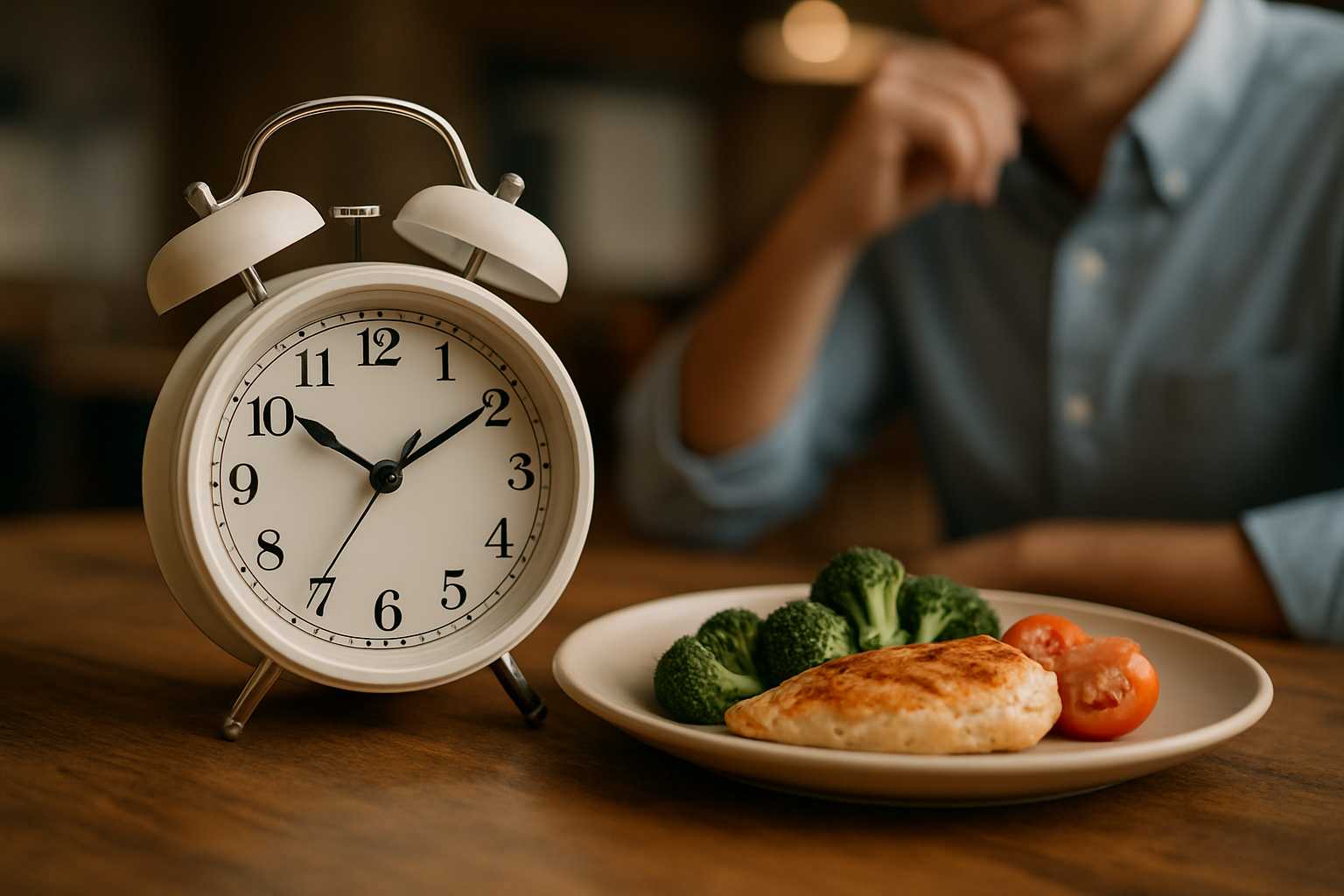

Circadian fasting, also known as time-restricted feeding, is based on the principle of aligning our eating patterns with our body’s natural circadian rhythm. This approach typically involves limiting food intake to a specific window of time each day, usually 8-12 hours, and fasting for the remaining hours. Unlike other forms of intermittent fasting, circadian fasting emphasizes consistency in meal timing rather than extended periods of calorie restriction.
The Metabolic Benefits of Circadian Synchronization
One of the most significant advantages of circadian fasting is its potential to optimize metabolic health. Studies have shown that eating in sync with our circadian rhythm can lead to improved insulin sensitivity, better glucose regulation, and enhanced lipid metabolism. This synchronization helps our bodies more efficiently process and utilize the nutrients we consume, potentially reducing the risk of metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Moreover, aligning our eating patterns with our circadian rhythm can positively impact our body’s cellular repair processes. During the fasting period, particularly overnight, our cells engage in autophagy, a crucial process where damaged cellular components are removed and recycled. This cellular housekeeping is essential for maintaining overall health and may play a role in longevity and disease prevention.
Circadian Fasting and Hormonal Balance
The timing of our meals can significantly influence our hormonal balance, particularly concerning melatonin and cortisol. Melatonin, often referred to as the sleep hormone, naturally increases in the evening to prepare our bodies for rest. Conversely, cortisol, known as the stress hormone, peaks in the morning to help us wake up and face the day’s challenges.
Circadian fasting can help reinforce these natural hormonal rhythms by avoiding late-night eating, which can disrupt melatonin production and interfere with sleep quality. By finishing meals earlier in the evening, we allow our bodies to transition into a state of rest and repair, potentially leading to improved sleep patterns and overall energy levels.
Implementing Circadian Fasting: Strategies and Considerations
Adopting a circadian fasting approach doesn’t necessarily mean drastic changes to your diet. The key is to establish a consistent eating window that aligns with your body’s natural rhythm. For many, this might involve eating breakfast slightly later and dinner earlier, creating a natural fasting period overnight.
A common strategy is the 16/8 method, where food intake is limited to an 8-hour window, such as 10 AM to 6 PM. This approach allows for three meals within the eating window while providing a 16-hour fasting period. However, it’s essential to remember that the specific timing can be adjusted to fit individual lifestyles and preferences.
It’s crucial to focus on nutrient-dense foods during the eating window to ensure adequate nutrition. Prioritize whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Hydration is also vital, and non-caloric beverages like water, herbal tea, and black coffee can be consumed during the fasting period.
Potential Challenges and Adaptations
While circadian fasting can offer numerous benefits, it’s not without challenges. Some individuals may experience hunger or irritability during the initial adjustment period. It’s important to start gradually, perhaps by extending the overnight fast by an hour or two, and then slowly increase the fasting duration over time.
For those with specific health conditions, such as diabetes or eating disorders, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before implementing any fasting regimen. Pregnant women, children, and individuals with a history of disordered eating should approach circadian fasting with caution and under medical supervision.
Circadian Wisdom: Practical Tips for Harmonious Eating
-
Aim to eat your last meal at least 3 hours before bedtime to support melatonin production
-
Expose yourself to natural light in the morning to reinforce your circadian rhythm
-
Stay consistent with your eating window, even on weekends, to maintain circadian synchronization
-
Listen to your body and adjust your eating window to align with your natural energy patterns
-
Incorporate protein-rich foods in your first meal to stabilize blood sugar and reduce cravings
As we continue to unravel the complexities of human physiology, circadian fasting emerges as a powerful tool for optimizing health and well-being. By aligning our eating patterns with our body’s natural rhythms, we can potentially unlock a host of benefits, from improved metabolic health to better sleep quality. As with any lifestyle change, the key lies in finding a sustainable approach that works for you, always prioritizing overall health and well-being above rigid rules. Embrace the wisdom of your body’s internal clock, and you may discover a new level of vitality and balance in your daily life.