Advancements in Wireless Communication Protocols
Wireless communication protocols are foundational to the modern digital landscape, enabling seamless connectivity across a vast array of devices and systems. From mobile phones to smart home gadgets, these underlying technologies facilitate the exchange of data, making everyday interactions faster, more efficient, and increasingly interconnected. Ongoing innovation in this field is critical for supporting the ever-growing demand for higher bandwidth, lower latency, and enhanced reliability in our connected world.

Evolution of Wireless Connectivity Technology
The landscape of wireless connectivity technology has undergone profound transformations, evolving from rudimentary radio transmissions to sophisticated modern protocols. Early forms of wireless communication laid the groundwork for transmitting voice and data over airwaves. The subsequent development of standards like Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11 family) revolutionized local area networking, while cellular generations (2G, 3G, 4G, and now 5G) have continually pushed the boundaries of mobile communication, offering faster speeds and broader coverage. Bluetooth, another key technology, has become indispensable for short-range device pairing. Each advancement addresses the growing demand for increased data rates, reduced latency, and greater spectral efficiency, driving continuous innovation in how devices connect and interact.
Impact on Modern Digital Devices and Gadgets
Modern digital devices and gadgets are intrinsically linked to the capabilities of wireless communication protocols. Smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, and other portable devices rely heavily on Wi-Fi and cellular networks for internet access and communication. Bluetooth enables seamless connections with accessories like headphones, keyboards, and fitness trackers. Furthermore, the proliferation of smart home devices, from lighting systems to security cameras, depends on robust wireless protocols to create interconnected ecosystems. These advancements not only enhance user convenience but also unlock new functionalities and applications, fundamentally reshaping how individuals interact with their personal electronics.
Enhancing Cybersecurity in Wireless Networks
As wireless connectivity becomes more pervasive, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures in wireless networks grows exponentially. Protecting data transmitted over the airwaves from unauthorized access, interception, and manipulation is paramount. Modern protocols incorporate advanced encryption standards, such as WPA3 for Wi-Fi, to secure communications and prevent eavesdropping. Authentication mechanisms ensure that only authorized devices can join a network. Despite these safeguards, the dynamic nature of wireless environments presents ongoing challenges, requiring continuous innovation in software and hardware to counter emerging threats and maintain data integrity and privacy across all connected devices.
Innovations in Hardware and Software for Wireless Systems
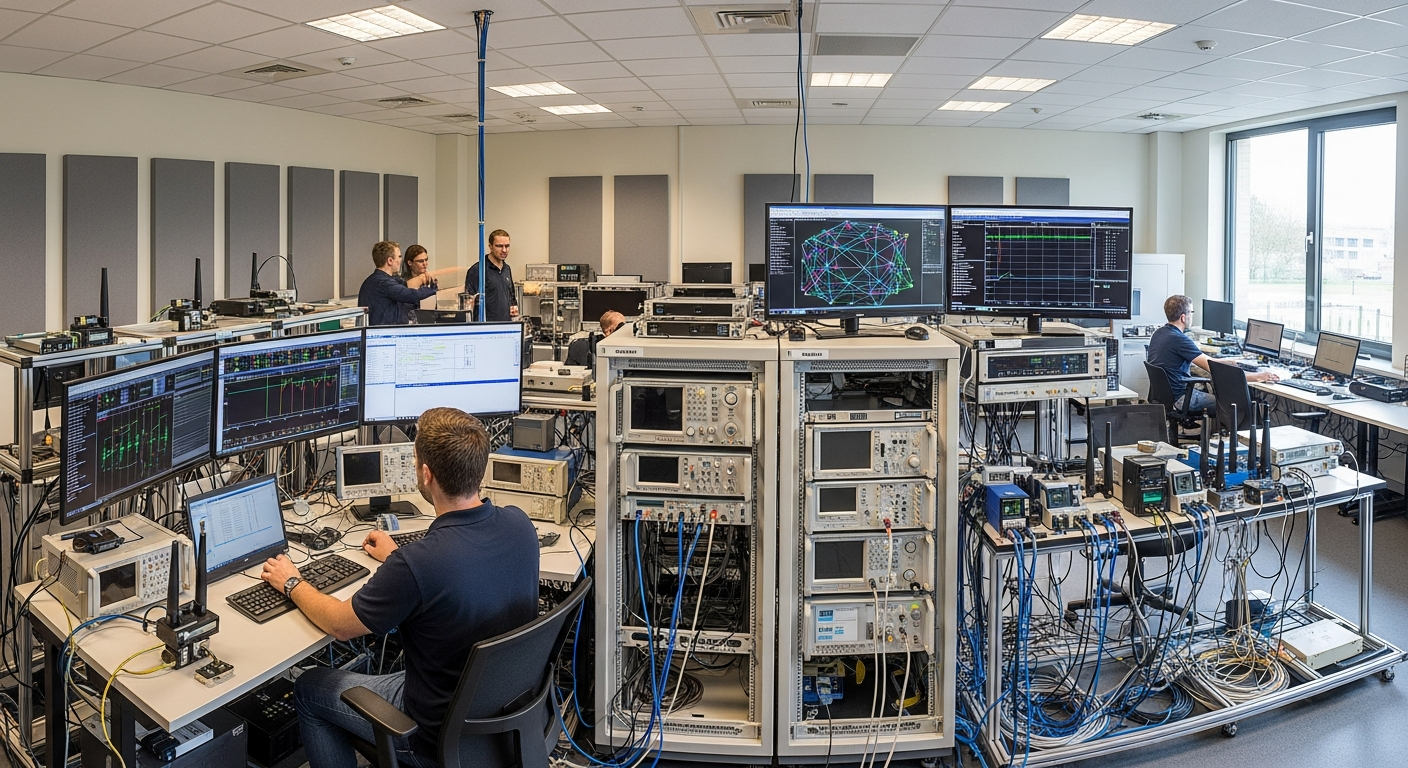
Progress in wireless communication is a direct result of concurrent innovations in both hardware and software. On the hardware front, advancements in chipsets, processors, and antenna designs enable devices to support multiple frequency bands, achieve higher data throughput, and consume less power. Specialized memory components are integrated to handle complex signal processing tasks efficiently. Simultaneously, sophisticated software algorithms optimize signal transmission and reception, manage network resources, and implement advanced error correction techniques. This synergistic development between physical electronics and digital programming is crucial for pushing the boundaries of what wireless systems can achieve, from improved range to enhanced reliability.
The Role of Wireless Protocols in Automation and IoT
Wireless protocols are fundamental enablers for automation and the vast ecosystem of the Internet of Things (IoT). In industrial settings, protocols like Wi-Fi 6 and 5G enable real-time data exchange for factory automation, predictive maintenance, and robotic control. For smart homes and buildings, protocols such as Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Thread provide low-power, mesh networking capabilities for sensors, actuators, and smart appliances, facilitating seamless automation. Long-range, low-power protocols like LoRaWAN are critical for wide-area IoT applications, including smart cities, environmental monitoring, and asset tracking. These diverse connectivity options support the widespread deployment of connected devices, driving efficiency and intelligence across various sectors.
Future Trends in Wireless Communication
The trajectory of wireless communication continues to point towards even greater speeds, lower latency, and expanded capabilities. Research and development are focused on next-generation cellular technologies beyond 5G, such as 6G, which aims to integrate artificial intelligence, holographic communication, and truly ubiquitous connectivity. Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) is on the horizon, promising multi-gigabit speeds and enhanced performance in congested environments. Furthermore, emerging technologies like Visible Light Communication (VLC) and advanced satellite internet are exploring new avenues for connectivity. These ongoing innovations are set to further integrate digital experiences into every aspect of life, enabling more complex applications and fostering a more connected world.